The current ratio indicates a companys ability to meet short-term debt obligations. 14 to hold enough HQLA to cover 30 days of net cash outflow.

Comparison Of Current Liquidity Ratio N5 And Liquidity Coverage Ratio Lcr Download Scientific Diagram

Weights Imposed Under The Basel Committee S Liquidity Coverage Ratio Download Table
Identifying Investing Cash Surpluses Ctmfile
The Liquidity Coverage Ratio and Corporate Liquidity Management.

Liquidity coverage ratio. Using the current ratio alone is not enough however. Section 20800 Funding Introduction Section 208005 Bank Holding Company Funding and Liquidity Section 40100 Parent Only Debt Servicing Capacity-Cash Flow. It is defined as the ratio between quickly available or liquid assets and current liabilitiesQuick assets are current assets that can presumably be quickly.
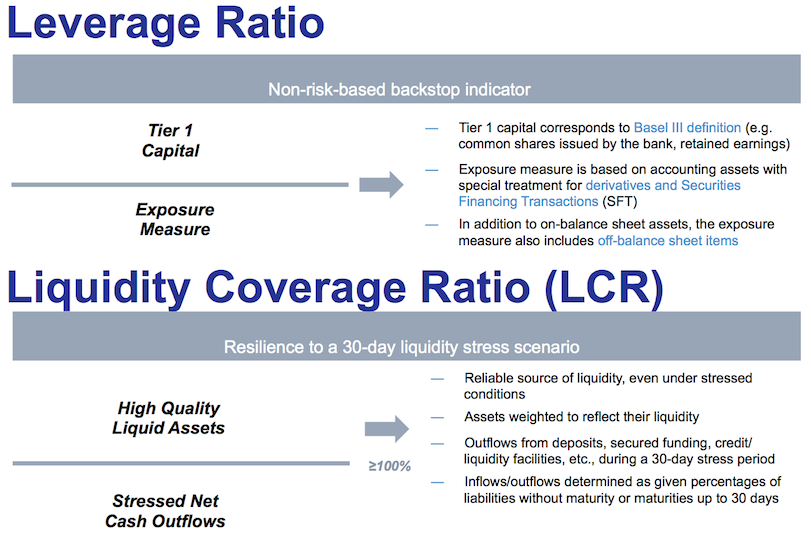
The liquidity coverage ratio should be expressed as a percentage and set at a minimum level of 100 when fully implemented which indicates that a credit institution holds sufficient liquid assets to meet its net liquidity outf lows during a 30-day stress period. Bank Holding Company Supervision Manual. Also a market characterized by the ability to buy and sell with relative ease.
Liquidity Coverage Ratio LCR for reporting entities operating in the Nigerian Banking Industry. Interest Coverage Ratio determines number of times the EBIT Earnings before interest and taxes of a company can cover its interest payments. Generally a ratio of 1.
The Basel Committee has issued the full text of the revised Liquidity Coverage Ratio LCR following endorsement on 6 January 2013 by its governing body - the Group of Central Bank Governors and Heads of Supervision GHOS. The Liquidity Coverage Ratio and liquidity risk monitoring tools January 2013. Large Bank Holding Companies BHC those with over 250 billion in consolidated assets or more in on-balance sheet foreign exposure and to systemically important non-bank financial institutions.
If your current ratio balance is less than 1 you may have to borrow money or consider the sale of assets to raise cash. Introduction 11 In the backdrop of the global financial crisis that started in 2007 the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision BCBS proposed certain reforms to. The LCR should be a key component of the supervisory approach to liquidity risk.
Within the mandatory SLR requirement Government securities to the extent allowed by the Reserve Bank under Marginal Standing Facility MSF are permitted to be reckoned as the Level 1 High Quality Liquid Assets HQLAs for the purpose of computing Liquidity Coverage Ratio LCR of. This ratio thus indicates the solvency of a firm. Liquidity Coverage Ratio.
Liquidity ratios greater than 1 indicate that the company is in good financial health and it is less likely fall into financial difficulties. Measured with liquidity ratios like current ratio. Most common examples of liquidity ratios include current ratio acid test ratio also known as quick ratio cash ratio and working capital ratio.
The proposal would require. The current ratio measures whether or not a firm has enough resources to pay its debts over the next 12 months. 1 is considered very comfortable because having a ratio of 1.
1 means the business is able to pay all of its current liabilities from the cash flow of its own operations. A higher current cash debt coverage ratio indicates a better liquidity position. In other words this calculation shows how easily a firms cash flow from operations can pay off its debt or current expenses.
During such a period a credit. Liquidity Risk Measurement Standards. The Committee has developed the LCR to promote the short-term resilience of the liquidity risk profile of banks by ensuring that they have sufficient HQLA to survive a significant stress scenario lasting 30 calendar days.
This note examines the changes in the liquidity management at banks and nonbank financial firms in the United States that occurred following the proposal of the liquidity coverage ratio LCR requirement in 2010 and its finalization in 2014. Liquidity ratios analyze the ability of a company to pay off both its current liabilities as they become due as well as their long-term liabilities as they become current. Liquidity ratio analysis helps in measuring the short-term solvency of a business.
The LCR is an essential component of the Basel III reforms which. Liquidity Coverage Ratio LCR is a requirement under Basel III whereby banks are required to hold enough high-quality liquid assets to fund cash outflows for 30 days. The Liquidity Coverage Ratio.
Current ratioefinition The current ratio is balance-sheet financial performance measure of company liquidity. Significance and interpretation. The LCR aims to promote short-term resilience of the liquidity risk profile of reporting entities by ensuring that they have an adequate stock of unencumbered high-quality liquid assets HQLA that can be.
In context of a corporation the ability of the corporation to meet its short-term obligations. Ratio analysis can be defined as the process of ascertaining the financial ratios that are used for indicating the ongoing financial performance of a company using few types of ratios such as liquidity profitability activity debt market solvency efficiency and coverage ratios and few examples of such ratios are return on equity current ratio quick ratio dividend payout ratio debt. The current ratio is a great metric to monitor liquidity and solvency.
The liquidity coverage ratio should be expressed as a percentage and set at a minimum level of 100 when fully implemented which indicates that a credit institution holds sufficient liquid assets to meet its net liquidity outflows during a 30-day stress period. Liquidity Coverage Ratio LCR Liquidity Risk Monitoring Tools and LCR Disclosure Standards Liquidity Coverage Ratio 1. In finance the quick ratio also known as the acid-test ratio is a type of liquidity ratio which measures the ability of a company to use its near cash or quick assets to extinguish or retire its current liabilities immediately.
The Liquidity Coverage Ratio applies to US. Liquidity Coverage Ratio LCR is a requirement under Basel III whereby banks are required to hold enough high-quality liquid assets to fund cash outflows for 30 days. In other words these ratios show the cash levels of a company and the ability to turn other assets into.
To manage cash effectively you need to monitor several other liquidity ratios. The interest coverage ratio is the ratio used to determine how many times can a company pay its interest with the current earnings before interest and taxes of the company and is helpful in determining liquidity position of the company by calculating how easily the company can pay interest on its outstanding debt. The cash flow coverage ratio is a liquidity ratio that measures a companys ability to pay off its obligations with its operating cash flows.
Notice 651 Liquidity Coverage Ratio Disclosure Requirements for domestic systemically important banks D-SIBs and internationally active banks to disclose information about their liquidity coverage ratio LCR and information relating to their internal liquidity risk measurement and management framework. Abstract of Basel III. Liquidity In context of securities a high level of trading activity allowing buying and selling with minimum price disturbance.
Banking operations with assets of more than 10 billion.
1

Liquidity Coverage Ratio Of Canadian Banks Download Table
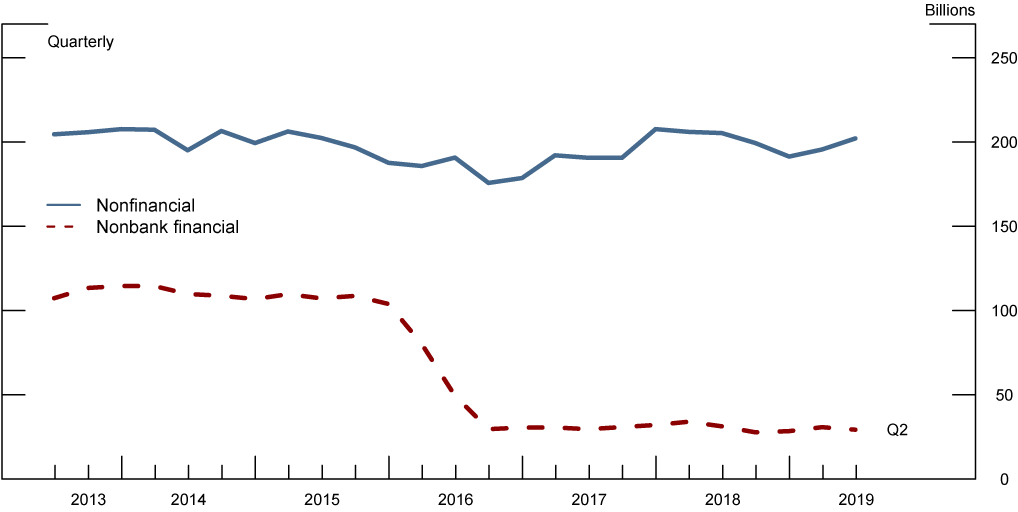
The Fed The Liquidity Coverage Ratio And Corporate Liquidity Management

Evolving Bank Regulation Basel Iii Liquidity Ppt Video Online Download
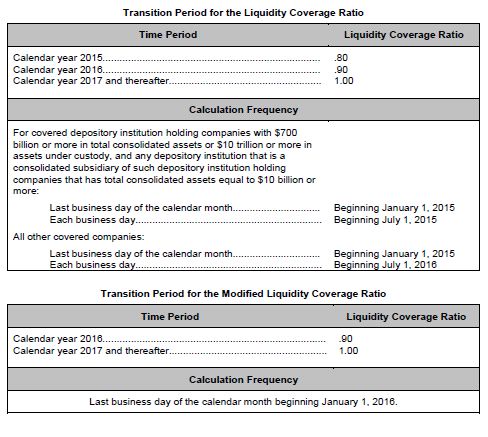
Liquidity Coverage Ratio A Quick Reference Finance And Banking United States

Liquidity Ratios Treas Risk Mngr

Artfully Dodging The Liquidity Coverage Ratio In Securities Lending And Repo Finadium

Liquidity Coverage Ratio An Analysis
- Memperpanjang Paspor Di Kjri Johor Bahru
- Confinement Centre In Klang Valley
- Ulul Azmi Nabi
- Happen To Be
- Nippon Express Penang
- Dark Jokes Reddit
- Malaysia Neighbouring Countries
- Flat Taman Jati Kulim
- 適 耕 莊
- Alanis Kota Warisan
- Bullring Shopping Centre
- External Hemorrhoids Stages
- Lada Sulah In English
- Realme 5 Pro Valentine
- undefined
- Ismail Abdul Rahman
- Tm Kuala Kubu Bharu
- Irwan Danny Mussry
- Honda Cb 150
- Uses Of Satellite
